Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) fuels not only the technological advancements in our businesses and homes but also redefines the operational frameworks of governments, military, and the broader societal constructs. The essence of this transformative power, however, finds its most compelling narrative in leadership and organizational health, where machine learning (ML), a subset of AI, plays a pivotal role. AI/ML can be used to support leaders in their efforts to manage and monitor initiatives and drive decisions. ML algorithms using continuous data collection activities can assist and support organization’s leaders through understanding if implemented initiatives are impacting operations by improving staff cross-collaboration and productivity while improving product and service innovation. Using predictive analytics to analyze trending data to predict future outcomes, leaders can determine if staying the course or pivoting in a certain direction is needed.
The Role of ML in Leadership
At the heart of leadership is the ability to foresee, adapt, and strategically steer organizations toward success. Powered by continuous data collection, ML algorithms offer leaders a mechanism for insight into their organizations. This provides data-driven insights that inform decision-making processes. Whether it is monitoring the efficacy of newly implemented initiatives or enhancing cross-collaboration among teams, ML stands as an ally for leaders. Its capacity to sift through vast amounts of data and identify patterns not only aids in improving operational efficiencies but also fosters product innovation by revealing untapped opportunities.
The predictive capabilities of ML, fueled by analytics, allow leaders to navigate their organizations with foresight. Analyzing trends and predicting future outcomes become instrumental in deciding whether to maintain the current trajectory or pivot in a new direction. This not only ensures agility and resilience in an ever-changing environment but also aligns organizational efforts with the most promising pathways to success.
Ethical Considerations in the Use of AI
As AI becomes increasingly integral to organizational strategy and decision-making, the importance of ethical considerations grows exponentially. Infusing AI solutions with ethical data practices is nonnegotiable. Leaders are tasked with the responsibility to ensure that AI is employed in a manner that respects privacy, promotes fairness, and prevents biases. The ethical deployment of AI underscores the commitment of an organization to responsible innovation and builds trust among stakeholders.
Ensuring that AI systems are developed and used in a way that promotes equality and fairness for the users and those effected by the AI system should be at the forefront of any AI system’s implementation as well as its ethical use and the ethical use of data. To ensure AI systems are developed with an ethical core, it is essential to start with establishing a diverse AI product development team that is active in designing, developing, and implementing the AI application [1]. A diverse team will bring a “diversity of thought” to the initiative and during the selection and cleansing of data to assist in removing bias from being a part of the algorithms used and ensure the models are trained with ethical data that adheres to privacy and security. Through collaboration, knowledge sharing, and knowledge reuse, a diverse team will bring different points of view, experiences, and cultural backgrounds to stimulate innovation and eliminate (or limit) bias. This action leads to innovation, which will enable organizations to deliver unique and/or improved AI products.
Leaders also need to be aware of the ethicality of AI applications being developed and deployed at their organizations. They must examine and understand whether the outcomes from applying AI violate U.S. federal, European Union General Data Protection Regulation, and/or other ethical, security, and privacy standards. Leadership will need to adopt a standard for AI that identifies general tenants for AI implementation focused on ethical adherence. Leaders must enable support for implementation, acceptance, and adoption of AI. Considerations for cultivating a system-thinking mindset and incorporating systems thinking, personal mastery, creation of mental models and a shared vision, and cultivation of team learning are essential for effective leadership of AI implementation.
Quality Data: A Critical Ingredient to Effective AI Solutions
For AI and ML to unlock their full potential, the foundation must be laid with quality data. The adage “garbage in, garbage out” holds particularly true in the context of AI. High-quality data not only enhances the accuracy of ML algorithms but also ensures that the insights generated are actionable and relevant. Leaders must prioritize establishing robust data collection and management systems that guarantee integrity and reliability of the data fed into AI systems [2].
The ethical use of data in AI applications is a critical issue, as AI systems and algorithms rely on data to learn and make decisions. The way data is collected, stored, used, and shared can have significant impacts on individuals, organizations, and society. Ethical use of data in AI systems builds trust and ensures that they are adopted and used in a responsible manner. Data ethics principles emphasize the importance of privacy, transparency, and responsibility in practices and provide guidelines for ensuring that data is collected, stored, and used in an ethical manner.
The following are key areas representing data ethic principles [2]:
- Transparency: Data ethics principles should be clear, open, and transparent to all stakeholders. This includes clearly stating the purpose and use of collected data, as well as providing information on how data is collected, stored, and protected.
- Fairness: Data should be collected and used in a way that is fair and nondiscriminatory. This includes ensuring that data collection does not perpetuate or exacerbate existing inequalities or biases.
- Privacy: Data privacy should be respected, and data should be collected and used in a way that protects individuals’ personal information and autonomy. This includes ensuring that data collection is done with informed consent and that it is not shared or used in ways that violate individuals’ privacy rights.
- Responsibility: Data collectors and users are responsible for ensuring that data is collected and used ethically. This includes being accountable for any harm that may result from collecting or using data and taking steps to mitigate that harm.
- Security: Data should be stored and transmitted securely to protect it from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
- Inclusivity: Data collection and use should be inclusive and considerate of diverse perspectives and experiences. This includes being aware of and addressing any potential biases in the data and actively seeking out underrepresented perspectives.
- Transparency in Decision-Making: Decisions that are made using data should be explainable and interpretable so that individuals can understand how and why decisions are being made and if any bias is present in the model.
- Continual Assessment: Organizations should regularly assess the ethical implications of their data collection and use practices and make any necessary changes to ensure they align with these principles.
Examining the Ethical Use of AI Applications
When examining the ethical use of AI, there are several key factors to consider. These factors align with the key areas representing data ethics principles. Having ethical data to train the algorithms contributes greatly to ensuring the AI solution delivers ethical results. The key factors in examining AI applications include the following [3].
Data Bias: The training data used to develop an AI model may contain biases that are then reflected in the model’s decisions and predictions. It is important to examine the data used to train the model and identify any potential sources of bias that may be present.
Algorithmic Bias: The algorithms and mathematical models used in AI can also be biased and may lead to biased decisions or predictions. It is important to examine the algorithms used in the AI system and identify any potential sources of bias that may be present.
Fairness: AI systems should be fair and nondiscriminatory and not perpetuate or exacerbate existing inequalities or biases. It is important to examine the AI system to ensure that it is not treating different groups of people unfairly.
Explainability: AI systems should be explainable so that individuals can understand how and why decisions are being made. It is important to examine the AI system to ensure that it is transparent and interpretable.
Privacy: The use of AI should respect privacy and personal autonomy and not violate individuals’ rights. It is important to examine the AI system to ensure that it is collecting and using data in a way that is consistent with privacy laws and regulations.
Transparency: The purpose and use of the AI system should be clear and open to all stakeholders. It is important to examine the AI system to ensure that it is transparent and that stakeholders are aware of how the data is being used.
Security: The AI system should be designed to protect data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. It is important to examine the AI system to ensure that it is secure and that data is being stored and transmitted securely.
Continual Assessment: Organizations should regularly assess the ethical implications of their AI use and make any necessary changes to ensure they align with these principles.
Having an AI ethics framework is essential for enabling the implementation and execution of ethics in an AI application (see Figure 1). This framework plays a significant role in ensuring that AI systems are developed and used in a way that is ethical, fair, transparent, and accountable. While the benefits of an AI ethics framework are clear, its implementation can be challenging. This requires a commitment to ongoing evaluation, the flexibility to adapt to new insights and circumstances, and the incorporation of diverse perspectives to address complex ethical dilemmas. Organizations must invest in education, training, and interdisciplinary collaboration to effectively implement an AI ethics framework and ensure that AI technologies serve the interest of the organization while respecting ethical norms and values.
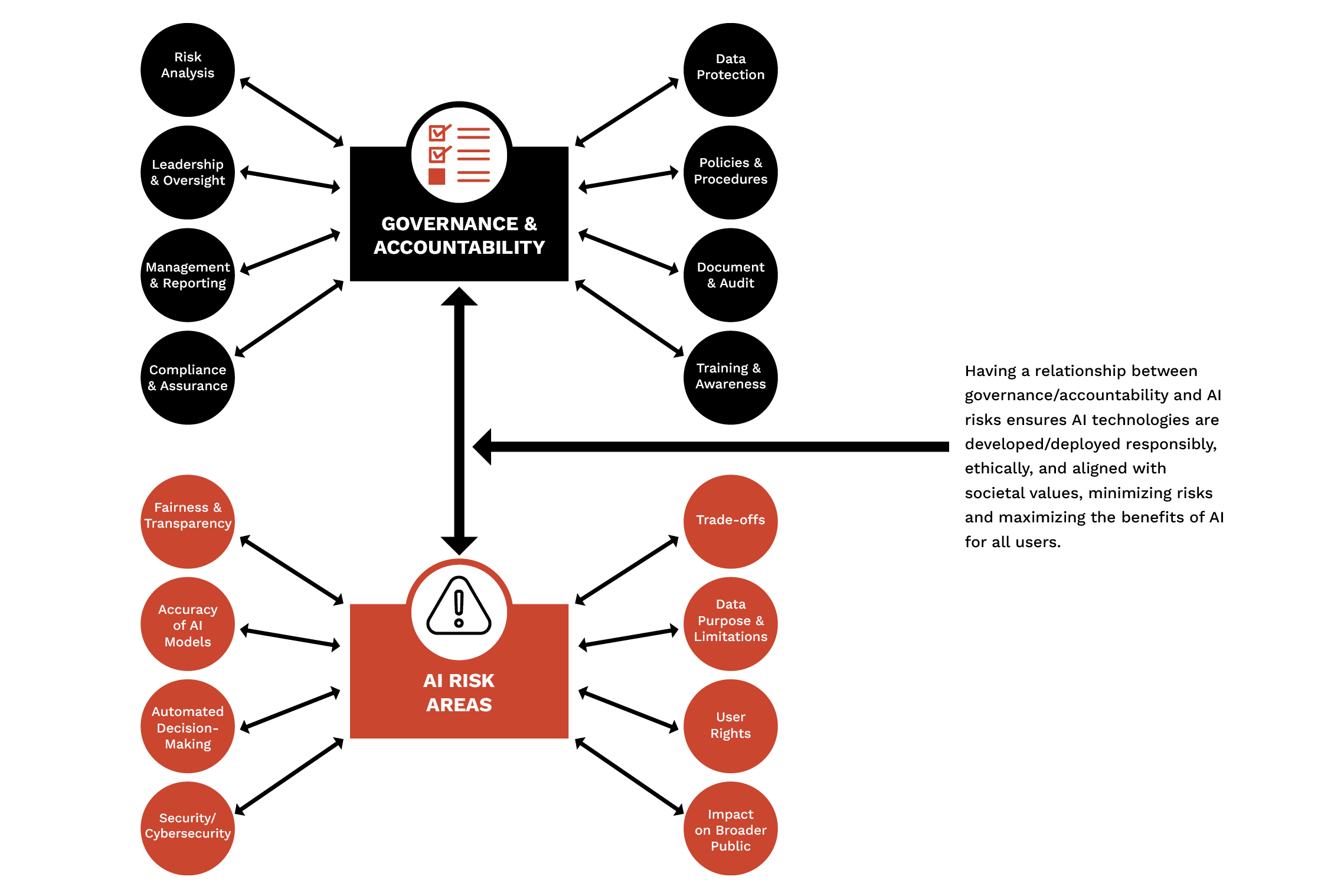
Figure 1. AI Ethics Framework Example (Source: A. Rhem).
Empowering Defense Leadership Through ML
AI has the potential to fundamentally transform the operational, strategic, and leadership paradigms within the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) and broader defense community. This transformation is rooted in the capabilities of ML, a subset of AI, which acts as a catalyst in enhancing decision-making, operational efficiency, and innovation in defense mechanisms [4].
Leadership within the defense sector is characterized by the necessity for rapid, informed, and strategic decision-making often under high-stake conditions. Through their ability to process and analyze vast datasets continuously, ML algorithms provide an unparalleled asset. For defense leaders, this translates into actionable intelligence—offering insights into operational readiness, threat detection, and resource allocation. ML’s predictive analytics capabilities enable the anticipation of potential threats and assessment of various strategic outcomes, thereby informing critical decisions that could shape the future security landscape.
Applying ML extends beyond strategic oversight and includes facilitating enhancements in cross-collaboration among different arms of the defense community. It supports integrating operations and optimizing logistics, ensuring that the defense apparatus functions as a cohesive and agile unit. Furthermore, by leveraging ML for product innovation, defense organizations can stay ahead of the technological curve, developing advanced defense solutions that ensure a competitive edge in national and global security arenas.
Ensuring Mission Success With Quality Data
The effectiveness of AI and ML within the defense community hinges on the availability of high-quality data. Accurate, timely, and relevant data is the lifeblood of AI systems, enabling them to deliver insights critical for mission success. From intelligence analysis to autonomous systems, cyber defense, and logistical support, high-quality data ensures AI-driven decisions are accurate and timely, which is vital in high-stakes scenarios where inaccuracies can lead to significant consequences. It enables real-time intelligence gathering, allowing military personnel to make informed strategic decisions and effectively plan operations. The DoD and defense organizations must prioritize establishing data curation processes and frameworks to ensure data integrity and security while applying ethical principles (see Figure 2) given the sensitive nature of defense operations.
![Figure 2. Ethical Data Curation Process (Source: Rhem [2]).](https://csiac.dtic.mil/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/rhem_figure-2.png)
Figure 2. Ethical Data Curation Process (Source: Rhem [2]).
Additionally, quality data drives the automation of routine tasks, such as surveillance and data analysis, freeing up personnel to focus on strategic duties and ensuring resources are utilized efficiently through optimized logistics and supply chains. Enhanced situational awareness and operational efficiency are direct benefits of quality data in military AI applications. It facilitates comprehensive analysis across various intelligence types, offering a holistic, operational view and improving planning and responsiveness. Powered by quality data, predictive analysis enables the anticipation of potential threats and changes, fostering a proactive stance in military operations. Moreover, the importance of quality data in the cyber realm extends to securing sensitive information and infrastructure, with AI systems relying on it to detect, identify, and effectively neutralize cyber threats.
The ethical use of AI in military operations, particularly in reducing collateral damage and ensuring compliance with international laws, underscores the necessity for quality data [5]. High-quality data is crucial for accurately identifying targets and minimizing unintended harm, thus supporting ethical considerations and bias mitigation in AI applications. This adherence to ethical standards and international norms is paramount in maintaining the legitimacy and effectiveness of military actions in the global arena.
The role of quality data extends to training and simulation, enhancing the realism of training programs and preparing military forces for various scenarios. It is also pivotal in developing, testing, and refining AI systems themselves, ensuring these technologies perform reliably under diverse conditions. Facing challenges like data security and integration, military organizations must prioritize advanced data management practices and foster collaborations to maintain a technological edge in the complex security landscape, highlighting the indispensable role of quality data in the effectiveness and ethical deployment of military AI solutions.
Implementing AI Solutions
Implementing AI solutions within military organizations involves a systematic and strategic approach to integrate advanced technologies with existing military operations, capabilities, and infrastructure [4]. The process requires careful planning, adherence to ethical standards, and consideration of operational, technological, and human factors.
Human factors are an important aspect of implementing AI solutions in the military and cover the physical and task conditions [6]. These factors refer to the study and application of psychological, physiological, and ergonomic principles to design systems, equipment, processes, and strategies that effectively integrate human capabilities and limitations [7]. Such factors will help safety personnel and members implement safety protocols. The aim is to enhance operational effectiveness, safety, and well-being in the challenging and often high-risk military environment. This interdisciplinary approach encompasses various aspects from the design of user-friendly technology and equipment to the optimization of training, team dynamics, and decision-making processes [7].
The development or acquisition of AI technology is a critical step, with military organizations needing to decide between in-house development, leveraging partnerships with industry and academia, or procuring off-the-shelf solutions [4]. This decision-making process should weigh the benefits of rapid access to cutting-edge technologies against the need for secure management of intellectual property and operational security. Rigorous testing and validation are essential to confirm that AI solutions meet stringent military requirements and can integrate smoothly with existing operational standards.
Integrating AI solutions into the military ecosystem requires careful attention to interoperability and operational integration. Ensuring that new AI technologies work seamlessly with legacy systems and complement existing tactics and procedures is crucial for their successful adoption. This stage involves significant adjustments, including upgrading outdated systems, training personnel to operate new AI tools effectively, and integrating AI technologies into live operations gradually. Training and change management are indispensable in this phase, equipping personnel with the necessary skills and addressing cultural and organizational resistance to change, thus facilitating a smooth transition to AI-enhanced operations.
Additionally, ongoing evaluation, adaptation, and cybersecurity are paramount for maintaining the effectiveness and security of AI applications in military contexts. Establishing mechanisms for real-time performance monitoring and creating feedback loops from operational use enable continuous improvement and rapid adaptation to emerging challenges. Robust cybersecurity measures protect sensitive AI systems from threats, while resilience planning ensures that military operations can persist in the face of AI system failures or adversarial threats. Through these comprehensive steps, military organizations can successfully implement AI solutions, leveraging them to achieve strategic advantages and operational excellence in modern warfare scenarios.
Conclusions
As the complexities of the 21st century are explored, the role of AI in enhancing organizational health, performance, and leadership cannot be overstated. It offers a path forward that is informed by data-driven insights, characterized by innovation, and guided by ethical considerations. Incorporating AI and ML into the strategic fabric of the defense community signifies a transformative shift. It presents an opportunity to redefine leadership, enhance operational effectiveness, and spearhead innovation in defense capabilities.
By leveraging AI and ML, defense leaders can ensure more informed decision-making, foster greater collaboration, and drive the development of next-generation defense technologies. As the defense community navigates this digital transformation, the focus must remain on harnessing the power of AI responsibly with a steadfast commitment to ethical principles and safeguarding global security. For leaders willing to embrace this journey, AI and ML not only promise a strategic edge but also the opportunity to redefine what is possible for military operations. The future of defense leadership is inherently linked to the intelligent integration of technology, promising a horizon where AI empowers the defense community to achieve unprecedented levels of readiness and resilience.
References
- AI Policy Exchange. “Anthony Rhem – How to Put AI Ethics into Practice.” Video, YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XW4Bc9LLR9Y, 17 October 2020.
- Rhem, A. J. “Ethical Use of Data in AI Applications.” Ethics – Scientific Research, Ethical Issues, Artificial Intelligence and Education, IntechOpen, pp. 95–108, https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.1001597, 2023.
- Baer, T., and V. Kamalnath. “Controlling Machine-Learning Algorithms and Their Biases.” McKinsey Insights, https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/risk/our-insights/controlling-machine-learning-algorithms-and-their-biases, 2017.
- Bistron, M., and Z. Piotrowski. “Artificial Intelligence Applications in Military Systems and Their Influence on Sense of Security of Citizens.” Electronics, vol. 10, no. 7, p. 871, https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10070871, 2021.
- Schraagen, J. M. “Responsible Use of AI in Military Systems: Prospects and Challenges.” Ergonomics, vol. 66, no. 11, pp. 1719–1729, https://doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2023.2278394, 2023.
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Human Factors in the Design of Tactical Display Systems for the Individual Soldier. Washington, D.C.: The National Academies Press, https://doi.org/10.17226/9107, 1995.
- van Diggelen, J., K. van den Bosch, M. Neerincx, and M. Steen. “Designing for Meaningful Human Control in Military Human-Machine Teams.” Research Handbook on Meaningful Human Control of Artificial Intelligence Systems, Edward Elgar Publishing, 2023.
Biography
Anthony J. Rhem is a thought leader, author, and consultant in AI, knowledge management (KM), big data, information architecture, and innovation. He has served as chief executive officer/principal consultant of A.J. Rhem & Associates Inc. (AJRA), a system integration consulting, training, and research firm specializing in KM and AI. Through AJRA, he and his staff work with Fortune 1000 companies and federal and state agencies to deliver technology solutions, strategies, governance, and architectures in AI and KM. Dr. Rhem holds a B.S. in marketing/computer science from Purdue University, an M.S. in computer science/AI from DePaul University, and a Ph.D. in KM from Walden University.


